About
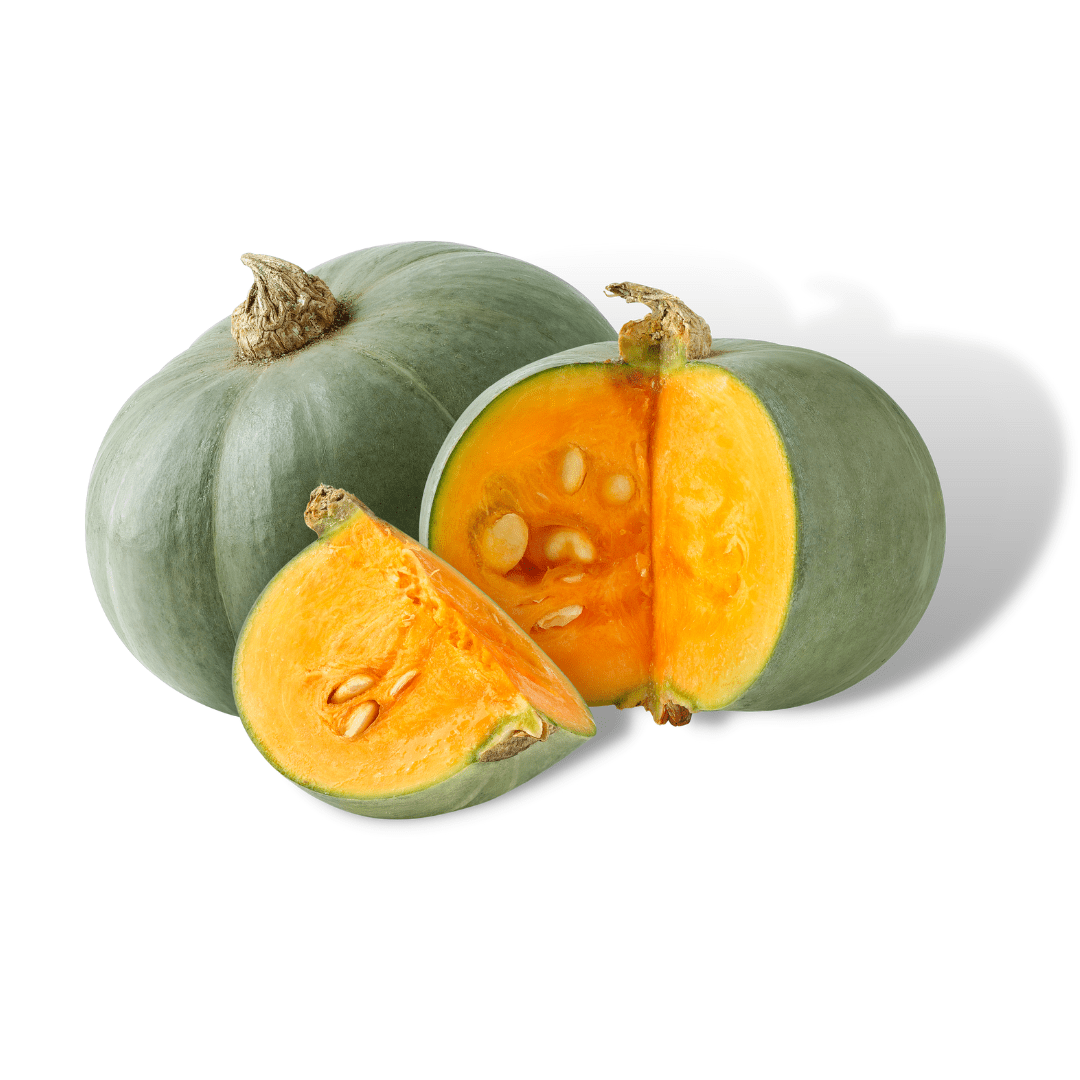
Squash is a vegetable that belongs to the family of Cucurbitaceae, and it comes in a variety of shapes, sizes, and colors. It is commonly consumed as a cooked vegetable or in soups, stews, curries, and salads. Squash is a nutrient-dense food that provides numerous health benefits.
Health benefits of Squash:
-
Rich in Nutrients: Squash is a good source of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, vitamin A, potassium, magnesium, and dietary fiber.
-
Promotes Digestive Health: Squash contains high amounts of dietary fiber, which promotes digestive health by improving bowel regularity, preventing constipation, and reducing the risk of colorectal cancer.
-
Boosts Immune System: Squash is a rich source of vitamin C, which helps to strengthen the immune system by protecting the body against infections, diseases, and free radicals.
-
Anti-inflammatory Properties: Squash contains antioxidants, such as beta-carotene, which helps to reduce inflammation in the body and prevent chronic diseases.
-
Helps to Control Blood Sugar: Squash contains complex carbohydrates and dietary fiber, which help to control blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of glucose in the bloodstream.
-
Promotes Heart Health: Squash is low in fat and cholesterol, making it an excellent food for promoting heart health. It contains high amounts of potassium, which helps to regulate blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Diseases that can be cured by Squash:
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Cancer
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Digestive Disorders
- Inflammation
Macro Nutrients found in 50g of Squash:
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrate | 3.5g |
| Fat | 0.2g |
| Protein | 0.8g |
| Fiber | 0.7g |
| Water | 44.1g |
Vitamins found in 50g of Squash:
| Vitamin | Amount |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 1285 IU |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.04mg |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.03mg |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.5mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.06mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 0mcg |
| Vitamin C | 6.5mg |
| Vitamin D | 0mcg |
| Vitamin E | 0.3mg |
| Vitamin K | 6.5mcg |
| Folate | 10.5mcg |
| Biotin | 0.3mcg |
Minerals found in 50g of Squash:
| Mineral | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calcium | 16.5mg |
| Iron | 0.3mg |
| Iodine | 1.0mcg |
| Zinc | 0.2mg |
| Magnesium | 13.5mg |
| Phosphorus | 20.0mg |
| Potassium | 167mg |
| Sodium | 1.5mg |
| Chloride | 36.5mg |
| Copper | 0.05mg |
| Chromium | 0mcg |
| Fluoride | 4.5mcg |
| Molybdenum | 1.5mcg |
What are the different types of squash?
There are various types of squash, including summer squash, winter squash, butternut squash, acorn squash, spaghetti squash, and more.
How to cook squash in various dishes?
Squash can be roasted, grilled, sautéed, stuffed, or used in soups, stews, casseroles, and even desserts.
Can squash be used in both sweet and savory dishes?
Yes, squash can be used in a wide range of recipes, from savory dishes like risotto to sweet treats like squash bread or pie.
How to roast squash for a caramelized flavor?
To roast squash, simply cut it into cubes or slices, toss with olive oil, salt, and pepper, and roast in the oven until tender and golden brown.
What are the health benefits of eating squash?
Squash is rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, and it provides dietary fiber, promotes healthy digestion, and supports a strong immune system.
How to incorporate squash into a healthy diet?
You can add squash to salads, stir-fries, grain bowls, or serve it as a side dish to boost the nutritional value of your meals.
What are the nutritional properties of squash?
Squash is low in calories and fat, high in fiber, and a good source of vitamins A, C, and E, as well as potassium and manganese.
Are there any specific squash recipes for weight management?
Squash can be a great addition to a weight management plan due to its low-calorie content, high fiber content, and filling properties.
How does squash contribute to a balanced diet?
Squash adds variety, flavor, and important nutrients to a balanced diet, helping to meet daily nutritional needs.
What are the different colors of squash and their characteristics?
Squash comes in various colors, including green, yellow, orange, and even striped or speckled varieties, each with its own flavor and texture.
How to choose and store squash for maximum freshness?
Look for squash with firm skin, no soft spots or bruises. Store them in a cool, dry place or in the refrigerator to extend their shelf life.
Can squash be frozen for later use?
Yes, squash can be frozen after blanching or cooking. This allows for easy preservation and future use in recipes.
What are the culinary uses of squash?
Squash can be used in a wide range of culinary creations, including soups, stews, salads, casseroles, side dishes, and even baked goods.
How to grow squash in a garden or container?
Squash can be grown from seeds or seedlings in a sunny spot with well-drained soil. They require regular watering and ample space for vine growth.
What are the farm-to-table benefits of squash?
Growing squash locally supports sustainable agriculture, reduces transportation emissions, and provides access to fresher and more flavorful produce.
How does squash support sustainable agriculture?
Squash requires less water and fewer pesticides compared to other crops, making it an environmentally-friendly choice for sustainable farming practices.