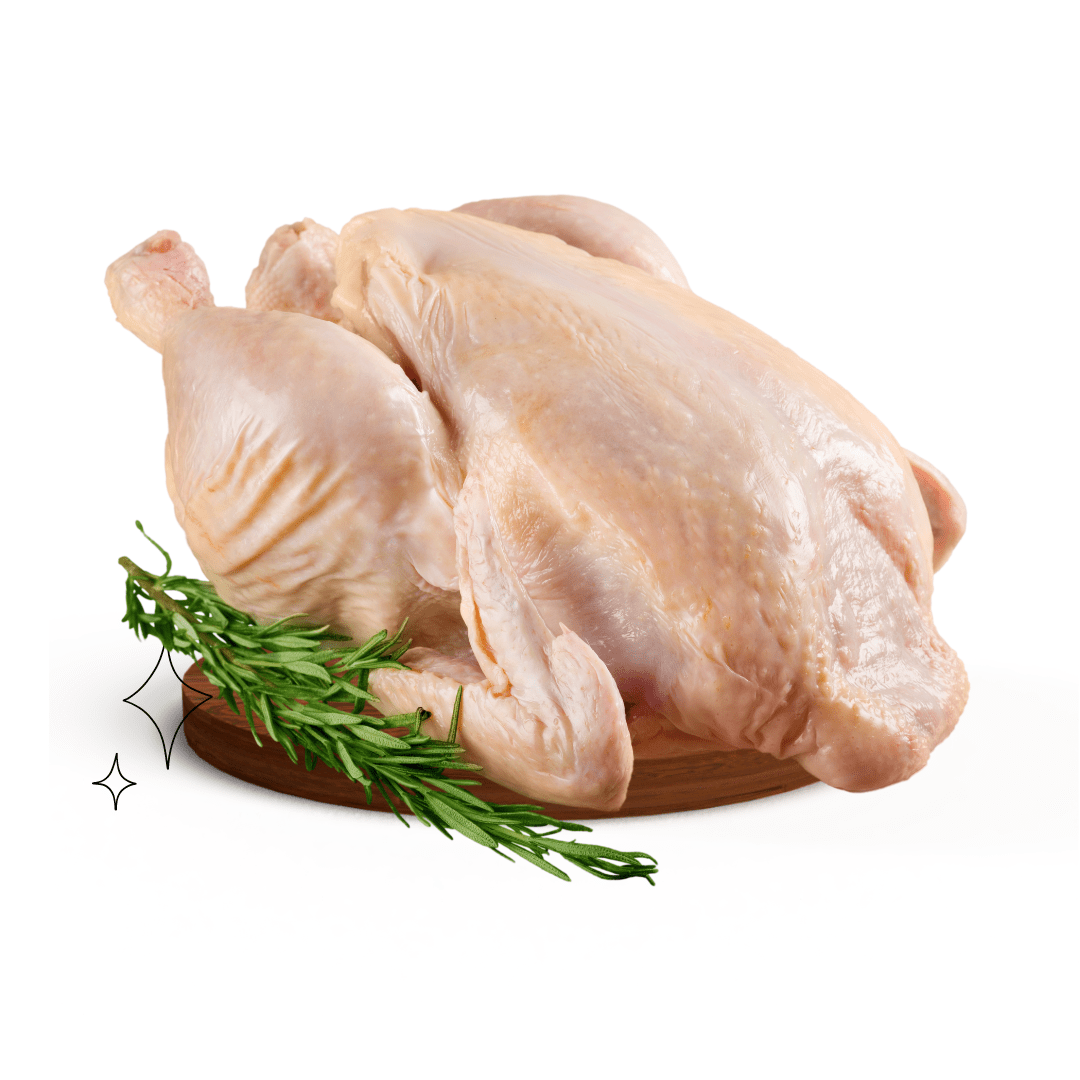
About
Chicken is a type of domesticated bird that is widely consumed around the world. It is a lean source of protein that is low in fat and calories, making it a popular choice for those looking to maintain a healthy diet.
Health Benefits of Chicken:
- Good source of protein: Chicken is a high-quality source of protein, containing all the essential amino acids that the body needs for growth and repair.
- Low in fat: Compared to other meats, chicken is relatively low in fat, which makes it a good option for those looking to manage their weight.
- Rich in vitamins and minerals: Chicken is a good source of several vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B6, vitamin B12, niacin, selenium, and phosphorus.
- Boosts immunity: Chicken contains zinc, which helps to boost the immune system and protect against infections.
- Promotes heart health: Chicken is a good source of niacin, which can help to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Health Risks of Chicken:
- Foodborne illness: If chicken is not cooked or handled properly, it can be contaminated with harmful bacteria like salmonella, which can cause foodborne illness.
- High in sodium: Some types of chicken, like processed chicken products, can be high in sodium, which can contribute to high blood pressure and other health problems.
Preparation Methods for Chicken:
- Grilled: Grilling chicken is a healthy way to cook it, as it allows the fat to drip away from the meat.
- Baked: Baking chicken is another healthy cooking method that allows the chicken to cook in its own juices, reducing the need for added fats or oils.
- Broiled: Broiling is a quick and easy way to cook chicken, as it cooks the meat quickly at high heat.
- Sauteed: Sauteing chicken in a small amount of oil or butter is a tasty way to cook it, but can add additional fat and calories to the dish.
Treatments for Chicken:
- Roasted: Roasting a whole chicken in the oven is a classic way to prepare this bird.
- Fried: Fried chicken is a popular dish in many cultures, but it can be high in fat and calories.
- Grilled: Grilling chicken is a healthy way to cook it, as it allows the fat to drip away from the meat.
- Stir-fried: Stir-frying chicken with vegetables and a small amount of oil is a tasty and healthy way to prepare it.
Harms of Overdose:
Consuming too much chicken can lead to overconsumption of protein and can increase the risk of developing health problems like kidney damage or osteoporosis. It is recommended to consume chicken in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Maximum Consumption Chart:
The maximum consumption of chicken per day depends on factors like age, sex, weight, and activity level. Here is a general guideline:
- Child: 1-2 servings (50-100 grams) per day
- Adult man: 2-3 servings (100-150 grams) per day
- Adult woman: 1-2 servings (50-100 grams) per day
Energy and Macronutrient Content per 50 grams of Chicken:
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | 80 |
| Protein | 9.6 g |
| Fat | 4.5 g |
| Carbohydrates | 0 g |
| Fiber | 0 g |
| Water | 35.9 g |
Vitamin Content per 50 grams of Chicken:
| Vitamin | Amount |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 10 µg |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.02 mg |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.06 mg |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.1 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.2 mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.3 µg |
| Vitamin C | 0 mg |
| Vitamin D | 0 µg |
| Vitamin E | 0.1 mg |
| Vitamin K | 0.1 µg |
| Folate | 2.5 µg |
| Biotin | 1.5 µg |
Mineral Content per 50 grams of Chicken:
| Mineral | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calcium | 5.1 mg |
| Iron | 0.5 mg |
| Iodine | 3.5 µg |
| Zinc | 0.7 mg |
| Magnesium | 7.3 mg |
| Phosphorus | 75.6 mg |
| Potassium | 86.4 mg |
| Sodium | 15.5 mg |
| Chloride | 22.4 mg |
| Copper | 0.02 mg |
| Chromium | 0.01 µg |
| Fluoride | 1.1 µg |
| Molybdenum | 2.2 µg |
| Manganese | 0.01 mg |
| Selenium | 10.9 µg |