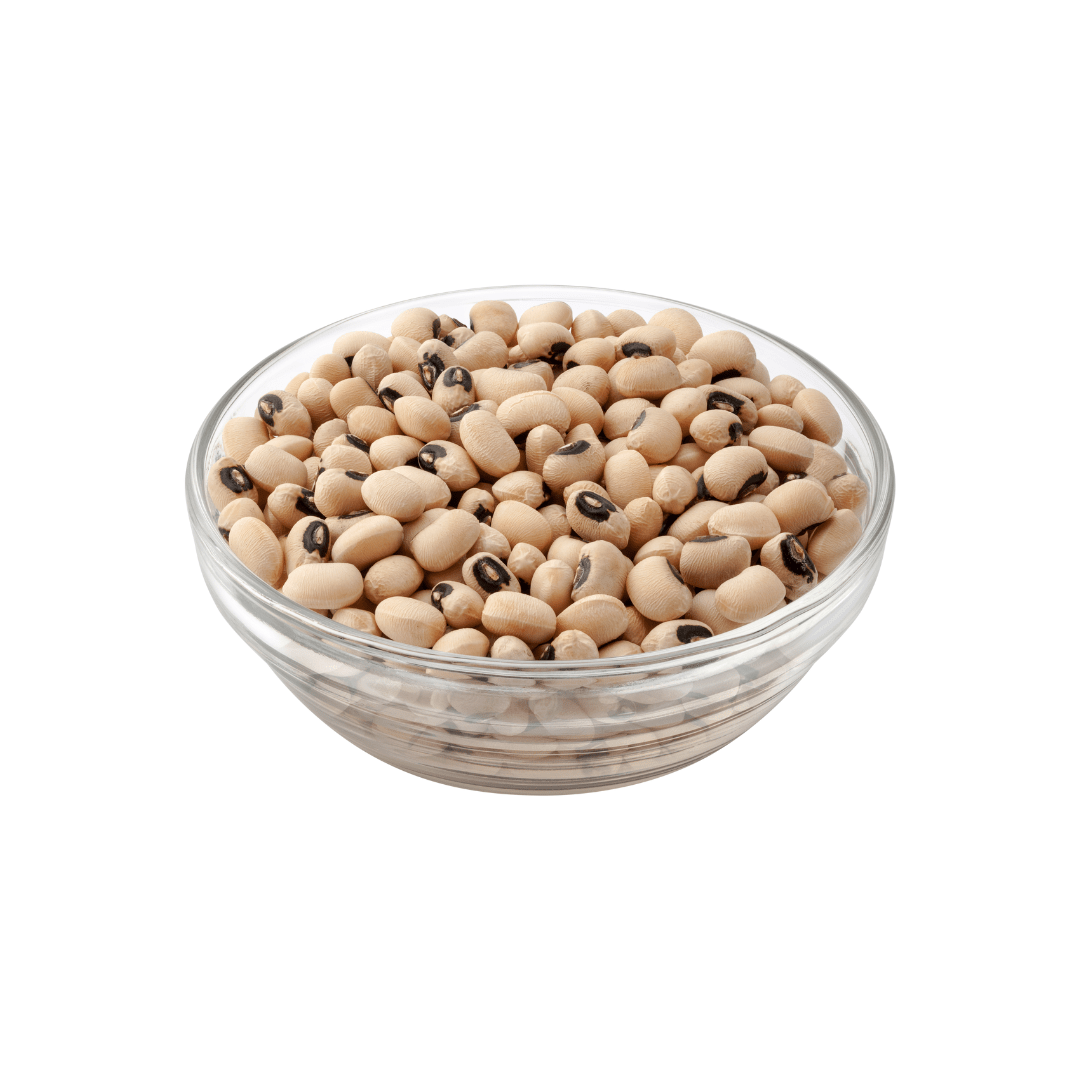
About
Black-eyed peas, also known as cowpeas, southern peas, or field peas, are a type of legume that is commonly used in Southern US cuisine. They are small, beige-colored beans with a distinctive black spot on one end, hence the name “black-eyed” peas.
Health Benefits of Black-eyed Peas:
-
Rich in Fiber: Black-eyed peas are an excellent source of dietary fiber, which can help regulate digestion and prevent constipation. Fiber also promotes feelings of fullness, making it easier to maintain a healthy weight.
-
High in Protein: Black-eyed peas are a good source of plant-based protein, which is important for maintaining muscle mass and supporting overall health.
-
Lowers Cholesterol: Black-eyed peas are rich in soluble fiber, which can help lower LDL or “bad” cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
-
Regulates Blood Sugar: The complex carbohydrates in black-eyed peas can help regulate blood sugar levels, making them a good choice for people with diabetes or those at risk of developing the disease.
-
Rich in Antioxidants: Black-eyed peas contain a variety of antioxidants, including flavonoids, carotenoids, and phenolic compounds, which can help protect the body against oxidative stress and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
List of diseases that can be cured:
While black-eyed peas cannot cure any diseases on their own, they can be part of a healthy diet that may help reduce the risk of certain health conditions, such as:
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- Cancer
- Obesity
- Digestive issues
Nutrient Content of Black-eyed Peas (per serving of 50g)
Energy and Macronutrient content of Black-eyed peas per serving (50g)
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | 57 |
| Carbohydrates | 10.8 g |
| Protein | 3.5 g |
| Fat | 0.2 g |
| Fiber | 2.7 g |
| Water | 33.2 g |
The vitamin content of Black-eyed peas per serving (50g)
| Vitamin | Amount |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 4 mcg |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 0.1 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 0.1 mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 0.7 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.1 mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 0 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 0.5 mg |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg |
| Vitamin E | 0.1 mg |
| Vitamin K | 1.4 mcg |
| Folate | 39.5 mcg |
| Biotin | 1.2 mcg |
Mineral Content of Black-eyed peas per serving (50g)
| Mineral | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calcium | 21.5 mg |
| Iron | 1.1 mg |
| Iodine | 0 mcg |
| Zinc | 0.7 mg |
| Magnesium | 23.5 mg |
| Phosphorus | 68.5 mg |
| Potassium | 139.5 mg |
| Sodium | 1.5 mg |
| Chloride | 5.5 mg |
| Copper | 0.1 mg |
| Chromium | 0 mcg |
| Fluoride | 0.5 mcg |
| Molybdenum | 7.5 mcg |
| Manganese | 0.3 mg |
| Selenium | 3.5 mcg |
What are black-eyed peas?
Black-eyed peas are a type of legume that is commonly used in Southern cuisine and is known for its mild, nutty flavor.
Are black-eyed peas healthy?
Yes, black-eyed peas are a healthy source of protein, fiber, and essential vitamins and minerals.
How do I cook black-eyed peas?
To cook black-eyed peas, rinse and soak them overnight, then simmer them in water or broth until tender.
What is Hoppin' John?
Hoppin' John is a traditional Southern dish made with black-eyed peas, rice, and pork or ham.
Can I make black-eyed peas in a crockpot?
Yes, black-eyed peas can be cooked in a crockpot for a hands-off, easy meal.
What are some traditional black-eyed peas dishes?
Besides Hoppin' John, black-eyed peas are commonly used in dishes such as stewed peas, black-eyed pea salad, and black-eyed pea dip.
How can I make black-eyed peas vegan?
Use vegetable broth instead of chicken or beef broth, and omit any meat or bacon that is traditionally used in the recipe.