About
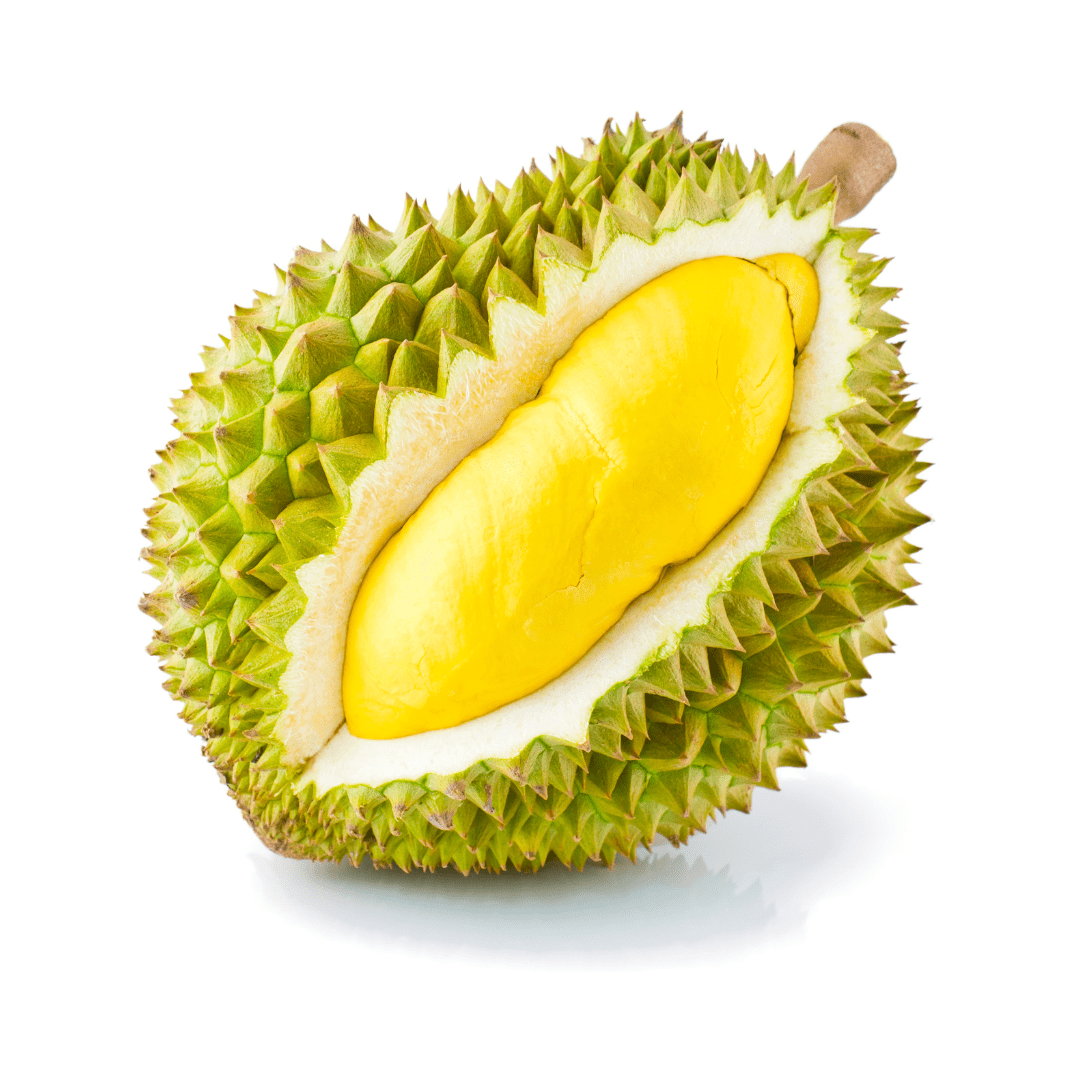
Durian is a tropical fruit with a spiky exterior and a creamy, custard-like interior. It has a strong odor and a unique taste, which some people describe as sweet and creamy, while others find it overpowering.
Here are some health benefits of Durian:
-
Rich in nutrients: Durian is rich in vitamins and minerals like vitamin C, potassium, and manganese.
-
Boosts immunity: The high vitamin C content in durian can help boost the immune system, and protect against infections and diseases.
-
Good for digestion: Durian is a good source of fiber, which can help promote healthy digestion and prevent constipation.
-
May reduce inflammation: Durian contains compounds that may help reduce inflammation in the body, which can lead to a lower risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
-
May improve skin health: The high vitamin C content in durian can help improve skin health by promoting collagen synthesis and reducing the appearance of wrinkles.
-
May improve bone health: Durian is a good source of calcium, which can help improve bone density and prevent osteoporosis.
-
May improve sleep: Durian contains tryptophan, an amino acid that can help promote relaxation and improve sleep quality.
List of diseases that can be cured by Durian:
- Constipation
- Diabetes
- Anemia
- High blood pressure
- Insomnia
- Respiratory problems
- Skin diseases
Here are the tables of macro and micronutrient content per 50-gram serving of Durian:
Macronutrient Content
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 23.8 g |
| Protein | 1.5 g |
| Fat | 3.9 g |
| Fiber | 2.3 g |
| Water | 19.5 g |
Micronutrient Content – Vitamins
| Vitamin | Amount |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 1,500 IU |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.2 mg |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.2 mg |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.5 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.2 mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.0 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 24.8 mg |
| Vitamin D | 0.0 IU |
| Vitamin E | 0.3 mg |
| Vitamin K | 3.0 mcg |
| Folate | 18.5 mcg |
| Biotin | 1.5 mcg |
Micronutrient Content – Minerals
| Mineral | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calcium | 11.5 mg |
| Iron | 0.4 mg |
| Iodine | 0.0 mcg |
| Zinc | 0.3 mg |
| Magnesium | 24.0 mg |
| Phosphorus | 29.0 mg |
| Potassium | 286.0 mg |
| Sodium | 2.5 mg |
| Chloride | 13.5 mg |
| Copper | 0.2 mg |
| Chromium | 0.0 mcg |
| Fluoride | 0.0 mcg |
| Molybdenum | 0.0 mcg |
What is Durian and its taste?
Durian is a tropical fruit known for its large size, spiky outer shell, and unique custard-like texture with a strong aroma and a sweet, creamy taste.
What are the health benefits of Durian?
Durian is rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, supporting immunity, promoting skin health, and aiding digestion.
What are the different Durian varieties?
Some popular Durian varieties include Musang King, D24, and Monthong, each having distinct flavors and characteristics.
Durian a superfood?
While not classified as a superfood, Durian's nutrient content and health benefits make it a nutritious choice.
Can Durian be used in desserts?
Absolutely! Durian's creamy texture and sweetness make it a popular choice for a variety of delectable desserts.
Are there any unique Durian flavors?
Yes, some Durian varieties offer unique flavor profiles, ranging from sweet and custard-like to slightly bitter or savory.
What are the nutritional values of Durian?
Durian contains essential nutrients like vitamin C, potassium, and dietary fiber, contributing to overall well-being.
How to incorporate Durian into a balanced diet?
Enjoy Durian in moderation as a part of a diverse diet that includes various fruits, vegetables, and whole foods.
What are the differences between Durian and other fruits?
Durian stands out with its spiky exterior, strong aroma, and rich, custard-like flesh, setting it apart from most fruits.
Are there any Durian allergies or sensitivities?
Some individuals may have allergic reactions to Durian due to its unique chemical compounds, so consumption should be approached with caution.
Can Durian be used in savory dishes?
Yes, in some Asian cuisines, Durian is used in savory dishes such as curries or mixed with rice and coconut milk.
What are some interesting facts about Durian?
Durian is often called the "King of Fruits," and its strong aroma has led to it being banned in some public places in certain countries.